- •₦800k and below = Tax-free. If you earn less than ₦800,000 per year, you pay nothing.
- •Progressive rates up to 25%. Higher earners pay more, but the maximum rate is 25% (up from 24% in the old system).
- •CRA is gone. The old Consolidated Relief Allowance has been discontinued.
- •Rent relief is new. You can claim up to 20% of your annual rent (maximum ₦500k) as a deduction.
- •VAT on essentials removed. Food, education, and healthcare attract 0% VAT.
- •No auto-debit. The government will not automatically deduct money from your account.
The Nigeria Tax Act 2025 (NTA 2025) represents the most significant overhaul of Nigeria's tax system in decades. Signed into law by President Bola Ahmed Tinubu on June 26, 2025, and effective from January 1, 2026, this new law consolidates multiple tax legislations into a single, unified statute.
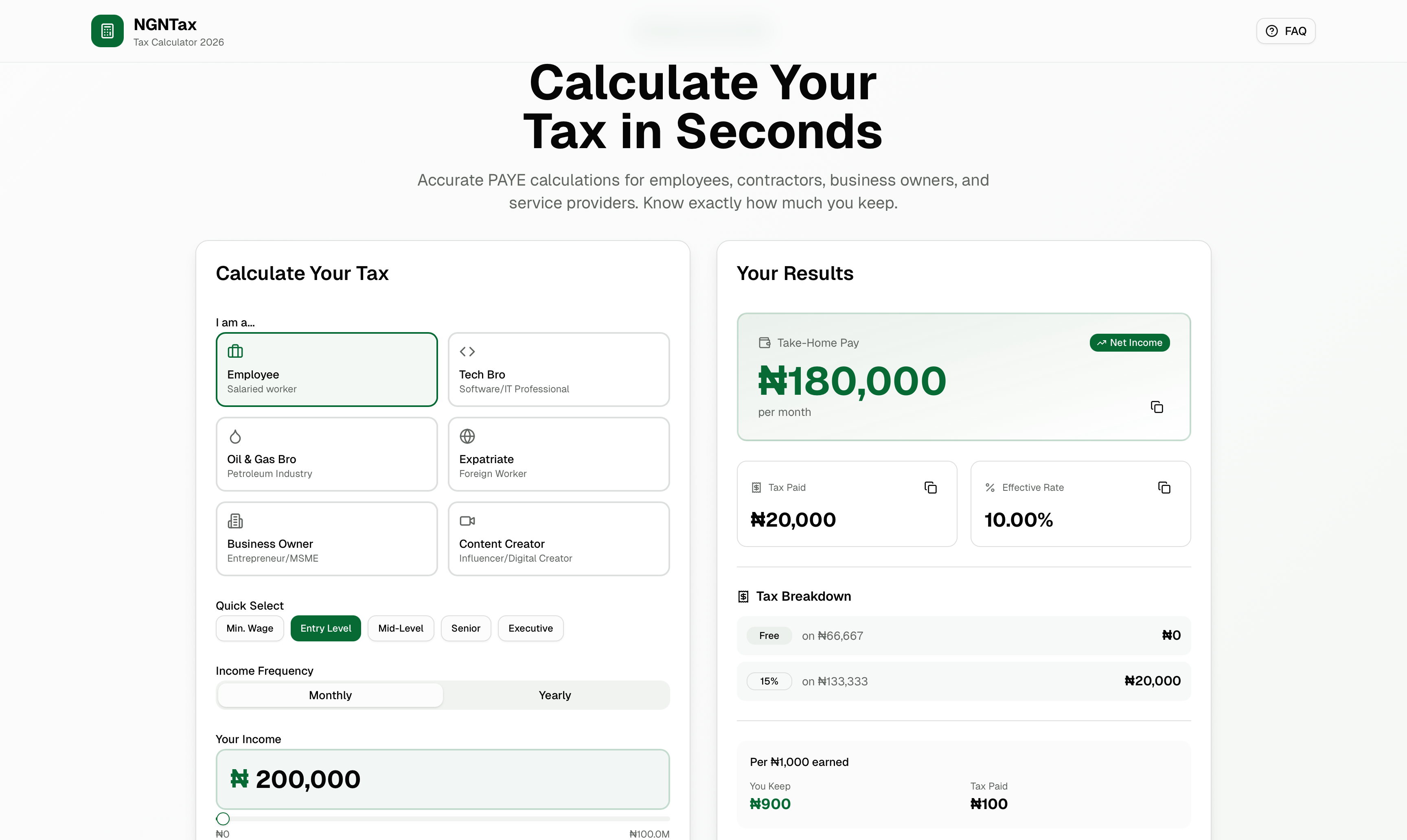
If you're wondering how your salary will be affected, we've built a free tax calculator that shows you exactly how much you'll keep and how much goes to tax.
What is the NTA 2025?
The Nigeria Tax Act 2025 consolidates several existing tax laws into one comprehensive framework:
- •Personal Income Tax Act (PITA)
- •Companies Income Tax Act (CITA)
- •Petroleum Profits Tax Act (PPTA)
- •Value Added Tax Act (VAT)
- •Capital Gains Tax Act (CGT)
The goal is to simplify compliance, broaden the tax base, and make the system fairer for everyone, especially low-income earners.
The New Tax Brackets
Under the NTA 2025, personal income tax follows a progressive structure with six brackets:
| Annual Income | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| ₦0 - ₦800,000 | 0% (Tax-Free) |
| ₦800,001 - ₦3,000,000 | 15% |
| ₦3,000,001 - ₦12,000,000 | 18% |
| ₦12,000,001 - ₦25,000,000 | 21% |
| ₦25,000,001 - ₦50,000,000 | 23% |
| Above ₦50,000,000 | 25% |
Important: These rates apply to your taxable income after deductions like pension and rent relief.
How PAYE Works Under NTA 2025
Pay-As-You-Earn (PAYE) is the system where your employer deducts income tax from your monthly salary and remits it to the tax authorities. Here's exactly how your tax is calculated:
Step 1: Calculate Gross Annual Income
Add all salary components: Basic Salary + Housing + Transport + Utilities + Leave Allowance + Other Benefits
Step 2: Calculate Pension Deduction
Minimum employee contribution is 8% of (Basic + Housing + Transport). This is deducted from your taxable income.
Step 3: Calculate Rent Relief
Take the lower of: (20% × Annual Rent Paid) OR ₦500,000. Requires rent receipts or lease agreement.
Step 4: Calculate Other Deductions
Include NHF (2.5% of Basic), NHIS, life insurance premiums with proper documentation.
Step 5: Calculate Chargeable Income
Gross Income - (Pension + Rent Relief + Other Deductions) = Chargeable Income
Step 6: Apply Tax Brackets
Apply the progressive tax rates to your chargeable income across each bracket.
Step 7: Calculate Monthly PAYE
Divide Annual Tax by 12 to get your monthly tax deduction.
Practical Example: How Tax is Calculated
Let's walk through a complete example to see exactly how your tax is computed under NTA 2025.
Given Information:
- • Monthly Salary: ₦300,000
- • Annual Gross Income: ₦3,600,000
- • Annual Rent Paid: ₦600,000
- • Pension Contribution: 8%
- • NHF Contribution: 2.5%
Step 1: Calculate Deductions
- • Pension (8% × ₦3,600,000) = ₦288,000
- • NHF (2.5% × ₦3,600,000) = ₦90,000
- • Rent Relief (20% × ₦600,000) = ₦120,000 (less than ₦500k cap)
- • Total Deductions = ₦498,000
Step 2: Calculate Chargeable Income
₦3,600,000 (Gross) - ₦498,000 (Deductions) = ₦3,102,000
Step 3: Apply Tax Brackets to ₦3,102,000
- • First ₦800,000 @ 0% = ₦0
- • Next ₦2,200,000 (₦800k to ₦3M) @ 15% = ₦330,000
- • Remaining ₦102,000 (₦3M to ₦3.102M) @ 18% = ₦18,360
- Total Annual Tax = ₦348,360
Step 4: Monthly PAYE
₦348,360 ÷ 12 = ₦29,030 per month
Summary:
- • Monthly Gross: ₦300,000
- • Monthly Tax: ₦29,030
- • Monthly Take-Home: ₦270,970
- • Effective Tax Rate: 9.68%
Who Doesn't Pay Tax?
The biggest news for everyday Nigerians: if you earn ₦800,000 or less per year (about ₦67,000 per month), you pay zero income tax.
This ₦800k threshold is a complete exemption, not just a deduction. It's designed to protect low-income workers from the tax burden.
Note on minimum wage: The current minimum wage is ₦70,000/month (₦840,000/year). This means minimum wage earners will pay a small amount of tax (about ₦6,000 per year or ₦500 per month) on the ₦40,000 above the threshold.
What Changed from the Old System?
Consolidated Relief Allowance (CRA): ABOLISHED
Under the old Personal Income Tax Act, you could claim a CRA of ₦200,000 fixed, plus 20% of your gross income. This has been completely removed.
Old CRA Formula: ₦200,000 + (20% × Gross Income) OR ₦200,000 + (1% × Gross Income), whichever is higher
New System: ₦800,000 tax-free threshold + Rent Relief
Rent Relief: NEW
A brand new rent relief system has been introduced to help tenants:
- •Relief amount: 20% of your annual rent paid
- •Maximum cap: ₦500,000 per year
- •Documentation required: Rent receipts or tenancy agreement
- •Who qualifies: Only tenants who actually pay rent (not homeowners or those living rent-free)
Example 1: Low Rent
Annual rent: ₦600,000 → Relief: ₦120,000 (20% × ₦600k)
Example 2: High Rent
Annual rent: ₦3,000,000 → Relief: ₦500,000 (capped at maximum)
Pension Contributions: Still Deductible
Pension contributions remain tax-deductible under NTA 2025:
- •Employee contribution: Minimum 8% of (Basic + Housing + Transport)
- •Employer contribution: Minimum 10% (not deductible from your tax)
- •Voluntary contributions: Up to 20% can be contributed, but only 8% minimum is mandatory
- •Tax benefit: Reduces your taxable income today; taxed only when withdrawn after retirement
Other Statutory Deductions Still Allowed
These deductions remain valid with proper documentation:
- •National Housing Fund (NHF): 2.5% of Basic Salary
- •NHIS (National Health Insurance): Contributions with proof
- •Life Insurance Premiums: With verifiable documentation
- •Approved Donations: To registered charities
How Different Taxpayers Are Affected
Tax Method: PAYE (Pay-As-You-Earn) - deducted by employer
Filing Deadline: Employers file by 10th of each month and annual returns by January 31st
Key Deductions: Pension (8%), NHF (2.5%), Rent Relief
Exemption: First ₦800k annual income is tax-free
Tax Method: Self-assessment - you calculate and file yourself
Filing Deadline: March 31st annually (or 6 months after financial year-end)
Taxable Income: Business profits, consulting fees, contract payments, dividends, capital gains, digital income
Withholding Tax: 5-10% may be withheld from payments (claimable as advance tax)
Minimum Tax: 1% of total gross income if annual income is low or loss is declared
Requirements: Must obtain TIN and register with FIRS self-service portal
Small Businesses: Gross turnover ≤ ₦50M and fixed assets ≤ ₦250M are EXEMPT from Companies Income Tax
Personal Income: Owner's salary/drawings are taxed as personal income using PAYE rates
Company Profits: Subject to Companies Income Tax (separate from personal tax)
New Levy: 4% Development Levy on assessable profits (replaces previous multiple levies)
Taxable Income: All digital income is now explicitly taxable under NTA 2025
Includes: YouTube AdSense, TikTok Creator Fund, Instagram sponsorships, affiliate marketing, online courses, digital products
Crypto & Forex: Virtual asset gains and trading profits are taxable
Filing: Must file as self-employed and obtain TIN
Important: Nearly every inflow is taxable unless specifically exempted
Will I Pay More or Less Tax?
For most Nigerians, the answer is less or nothing at all. Here's how different income levels are affected:
| Monthly Salary | Old System (Est.) | New NTA 2025 | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| ₦50,000 | ~₦0 | ₦0 | Same |
| ₦100,000 | ~₦8,000 | ~₦3,500 | -56% |
| ₦300,000 | ~₦30,000 | ~₦28,000 | -7% |
| ₦500,000 | ~₦75,000 | ~₦63,000 | -16% |
| ₦1,000,000 | ~₦175,000 | ~₦143,000 | -18% |
Note: These are estimates. Use our tax calculator for your exact figures.
Tax Filing Requirements & Deadlines
All taxable persons (individuals, businesses, companies, NGOs) MUST register for a Tax Identification Number (TIN) before operating any taxable activity.
Penalty for non-registration: ₦50,000 for first month + ₦25,000 for each subsequent month
Filing Deadlines for Employees
Monthly PAYE Remittance (by Employers)
Due: 10th day of the month following salary payment
Penalty: 10% of tax due + CBN interest rate
Annual Tax Returns (by Employers)
Due: January 31st each year
Penalty: 10% of tax due + CBN interest rate